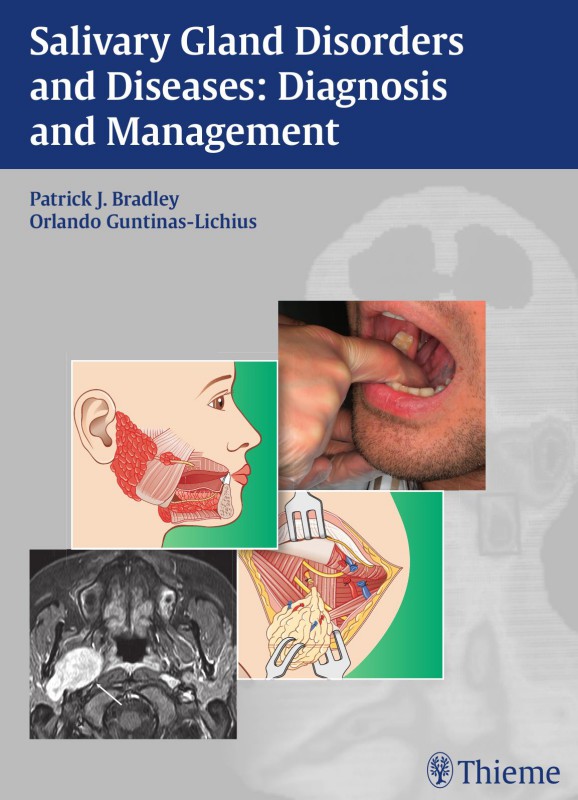
Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases Diagnosis and Management 1st Edition by Patrick J Bradley, Orlando Guntinas Lichius ISBN 3132578967 9783132578968
$50.00 Original price was: $50.00.$25.00Current price is: $25.00.
Authors:Bradley, Patrick J.; Orlando Guntinas-Lichius , Author sort:Bradley, Patrick J.; Orlando Guntinas-Lichius
Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases Diagnosis and Management 1st Edition by Patrick J Bradley, Orlando Guntinas Lichius – Ebook PDF Instant Download/Delivery. 3132578967, 9783132578968
Full download Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases Diagnosis and Management 1st Edition after payment
Product details:
ISBN 10: 3132578967
ISBN 13: 9783132578968
Author: Patrick J Bradley, Orlando Guntinas Lichius
Salivary glands are unique because of the manifold subtypes of benign and malignant diseases found there. Written by world-renowned experts, Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases: Diagnosis and Management fills a major gap in the literature by presenting modern and up-to-date knowledge on all aspects of this important field.
From new findings at the molecular level, to diagnostic advances in cytopathology, histopathology, biochemistry, and imaging studies, to technical innovations and surgical and medical management, the book covers every diagnostic and therapeutic development and innovation. Its clear, concise, and heavily illustrated approach makes it ideal for use by both beginners and more experienced surgeons and physicians.
Features:
- Covers the full spectrum of infectious, inflammatory, acute, chronic, benign, and malignant disorders and diseases of the salivary glands
- Offers a wealth of expert tips, tricks, pitfalls, and recommendations for effective diagnostic, surgical, and medical management
- Highlights all topics with hundreds of full-color images, diagrams, and superbly detailed surgical illustrations
As the comprehensive reference in the field, this book is essential for head and neck surgeons, otorhinolaryngologists, maxillofacial surgeons, dentists, oral pathologists, plastic surgeons, and any other clinicians involved in daily clinical management of patients with salivary gland disorders and diseases.
Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases Diagnosis and Management 1st Table of contents:
Section I Salivary Glands—Anatomy and Evaluation
1 Embryology and Clinical Anatomy
Introduction
Clinical Anatomy
Embryology
2 Regulatory Mechanisms and Salivary Gland Functions
Introduction
Functions of Saliva
Spontaneous and Reflex Secretion
Stimulus for Reflex Secretion
Salivary Centers—Facilitation and Inhibition
Efferent Pathways—Nontraditional Routes
Neural Control of Salivary Gland Activity
Hormonal Influences
Sensory Innervation
Early and Late Denervation Phenomena
Gland Weight
Effects of Aging
Pharmacological Aspects
3 Evaluation of Saliva—Normal and in Disease
Introduction
Effect of Stimulation on Ion Composition and the Secretion Rate
Effect of Stimulation on Protein Composition
Salivary Collection Procedures
Diseases of the Salivary Glands and Saliva
Saliva as a Diagnostic Tool for Other Diseases
4 Contemporary Salivary Clinical Pathology—Facts and Dilemmas
Introduction
Normal Structural Variations
Inflammatory Diseases
Cystic Diseases
Benign Epithelial Tumors
Malignant Epithelial Tumors
Nonepithelial Tumors and Metastases
5 Methods of Investigation
Introduction
Examining the Patient
Examining Saliva
Ultrasonography
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
Sialendoscopy
Salivary Gland Biopsy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography
Classic Sialography and Magnetic Resonance Sialography
Salivary Gland Scintigraphy
Serologic Examinations
6 Patient History and Clinical Examination
Introduction
Patient History
Clinical Examination
Ultrasonography
7 Evaluation of Salivary Glands—Imaging
Introduction
Conventional Radiography
Conventional Sialography
Radionuclide Scanning
Ultrasonography
Computed Tomography
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MR Sialography
PET/CT
8 Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Frozen Sections in Salivary Gland Diseases
Introduction
Informed Consent
Equipment Required
Physician
Aspiration Techniques
Slide Preparation
Fixation Techniques
Staining Methods
Complications
Contraindications
Accuracy
The Role of Frozen-Section Diagnosis
The Role of Core-Needle Biopsy
9 Diagnostic Sialendoscopy
Introduction
Definition
Sialendoscopic Anatomy
Patient Selection for Sialendoscopy
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Learning Sialendoscopy
Anesthesia
Equipment
Operative Steps
Contraindications
Complications
Postoperative Care
Scope Sterilization: Autoclave, Gas, Soaking
Section II Pediatric Disorders
10 Congenital and Developmental Abnormalities
Introduction
Epidemiology
Diagnostic Work-Up
Salivary Gland Aplasia and Duct Abnormalities
Congenital Vascular Anomalies
First Branchial Cleft Anomalies
Parapharyngeal Cysts
Pediatric Salivary Gland Surgery
11 Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Introduction
Epidemiology and Etiology
Differential Diagnosis of Neoplasms
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Histopathological Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Management of Recurrent Neoplasms
Outcomes and Prognosis
12 Drooling
Introduction
Definition
Epidemiology and Etiology
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Differential Diagnosis
Surgical Treatment
Nonsurgical Treatment: Botulinum Toxin Injection
Outcome and Prognosis
13 Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases of the Salivary Glands
Introduction
Definition
Epidemiology and Etiology
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Treatment
Parenchymal Infections
Intrasalivary Lymphadenopathy
Noninfective Conditions
Section III Physiological Disorders
14 Dry Mouth and Dry Eyes
Dry Mouth—Xerostomia and Hyposalivation
Dry Eyes
15 Sialadenitis and Sialadenosis—Interventional Sialendoscopy
Introduction
Definition
Indications and Patient Selection
Diagnostic Work-Up
Contraindications
Patient Information and Consent
Anesthesia and Positioning
Equipment
Procedural Steps
Complications
Postoperative Care
16 Autoimmune Disorders, Lymphoproliferation, and Granulomatous Inflammation
Introduction
Sjögren Syndrome (Autoimmune Sialadenitis, Mikulicz Disease, Chronic Sclerosing Sialadenitis)
MALT Lymphoma
Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Sarcoidosis
HIV Infection
17 Cystic Salivary Gland Tumors Including Cystic Neoplasms
Introduction
Definition
Clinical Classification of Cysts
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Benign Salivary Cysts
Mucoceles
HIV–Associated Salivary Cysts
Branchial Cleft Cysts
Ranulas
Cystic Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Lymphoma
Neurological Neoplasms
Other Causes
Section IV Benign Salivary Gland Neoplasms
18 Epidemiology of Benign Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Introduction
Etiology of Benign Salivary Gland Tumors
Classification
Data and Site Distribution
Incidence Reports of Benign Salivary Tumors
19 Etiology
Introduction
Radiation
Viruses
Other Environmental Risk Factors
Genetics
20 Classification of Benign Salivary Neoplasms
Introduction
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Warthin Tumor
Myoepithelioma
Basal Cell Adenoma
Oncocytoma
Canalicular Adenoma
Sebaceous Adenoma
Sebaceous and Nonsebaceous Lymphadenomas
Ductal Papillomas
Cystadenoma
Benign Nonepithelial Tumors and Tumorlike Lesions
21 Investigation
Introduction
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Preparation and Scheduling of Surgery
22 Surgical Management
Introduction
Surgical Anatomy of the Parotid Gland and Parapharyngeal Space
Surgical Anatomy of the Submandibular Gland
Surgical Anatomy of the Sublingual Gland
Surgical Anatomy of the Minor Salivary Glands
Indications and Patient Selection
Patient Information and Consent
Anesthesia and Positioning
Operative Steps—Parotid Gland
Operative Steps—Submandibular Gland
Operative Steps—Sublingual Gland
Operative Steps—Minor Salivary Glands
Tips and Tricks in Salivary Surgery
Complications
Postoperative Care
Outcomes
23 Radiotherapy
Introduction
Clinical Presentation
Treatment
Indications and Patient Selection for Radiotherapy
Patient Information and Consent
Radiotherapy Treatment Technique for Electrons
Radiotherapy Treatment Technique for Photons
Radiotherapy Dose
Outcome and Prognosis
Complications and Limitations
24 Recurrent Benign Salivary Tumors
Introduction
Epidemiology and Etiology
Diagnostic Work-Up
Surgery for Benign Recurrent Disease
Operative Steps
Complications
Postoperative Care
Postoperative Radiotherapy for Benign Recurrent Disease
Section V Malignant Salivary Gland Neoplasms
25 Epidemiology of Malignant Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Introduction
General Concepts and Complexities
Problems in the Published Epidemiological Data
Institutional Studies
Databases and Population-Based Studies
26 Etiology
Introduction
Radiation
Viruses
Lifestyle and Nutrition
Occupation
Hormones
Genetics
27 Malignant Salivary Gland Neoplasms—Classification
Introduction
Histogenesis of Malignant Salivary Gland Neoplasms
TNM and Stage Groupings
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Polymorphous Low-Grade Adenocarcinoma
Oncocytic Carcinoma
Salivary Duct Carcinoma
Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma
Other Rare Salivary Gland Malignancies
28 Imaging Examinations
Introduction
Choice of Imaging Method
Ultrasound Features of Salivary Gland Malignancies and Differential Diagnosis
CT Features of Salivary Gland Malignancies and Differential Diagnosis
MR Features of Salivary Gland Malignancies and Differential Diagnosis
Features on FDG–PET/CT
29 Surgical Management
Introduction
Indications and Patient Selection
Choice of Surgical Procedure
Informed Consent
Anesthesia and Positioning
Surgical Steps
Postoperative Radiotherapy
Complications and Sequelae of Surgery
Measures for Specific Complications
Postoperative Care
Outcomes
Follow-Up after Curative Surgery
30 Radiotherapy
Introduction
Patient Selection
Indications for Radiotherapy
Results of Local and Locoregional Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy Techniques
Future Directions
31 Chemotherapy and Novel Therapeutics
Introduction
Epidemiology and Etiology
Molecular Biology of Salivary Gland Cancer
Clinical Features
Indications and Patient Selection
Diagnostic Work-Up
Treatment
Outcomes and Prognosis
32 Neck Metastasis
Introduction
Prognostic Impact of Lymph-Node Metastases
Incidence of Clinically Detectable Neck Metastases
Occult Metastases
Neck Recurrences
Treatment of the Node-Positive Neck
Treatment of the Node-Negative Neck
Neck Dissection Surgery
Complications of Neck Dissection
33 Locoregional Recurrence and Its Management
Introduction
Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Recurrence
Diagnostic Work-Up
Surgery for Local Recurrence
Surgery for Regional Recurrence
Radiotherapy for Locoregional Recurrence
Chemotherapy or Biological Agents for Locoregional Recurrent Disease
34 Distant Metastases and Management
Introduction
Basic Mechanisms of Metastasis
Clinical Features and Pathological Aspects
Follow-Up
Diagnostic Work-Up
Treatment
35 Prognostic Index for Overall Disease Control in Patients with Parotid Carcinoma
Introduction
Overview of Prognostic Research
Disease-Specific Survival in Patients
Results of Univariate and Multivariate Survival Analysis
Interpretation of P Values
Development of a Prognostic Index for Disease Control
External Validation of the Prognostic Index
Limitations of the Current Prognostic Index System
Future Developments in Prognostic Research
Section VI Other Topics
36 Malignant Head and Neck Tumors and Skin Cancer Infiltrating the Parotid Glands
Introduction
Parotid Lymph Nodes and Skin Cancer
Parotid Lymph-Node Metastasis and Cervical Lymph Nodes
Risk Factors for Lymphogenic Metastasis of Skin Cancer
Prognosis
Follow-Up in High-Risk Patients
Treatment
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Malignant Melanoma
Parotid Lymph-Node Metastases from Noncutaneous Head and Neck Cancer
Direct Invasion of the Parotid by Head and Neck Cancer
37 Metastases to the Major Salivary Glands from Non–Head and Neck Primary Malignancies
Introduction
Metastases to the Parotid Gland
Metastases to the Submandibular Gland
38 Principles of Facial Reanimation Surgery
Introduction
Direct Facial–Facial Nerve Reconstruction
Facial–Facial Nerve Interpositional Graft
Hypoglossal–Facial Nerve Jump Anastomosis and Combined Approach
Upper Eyelid Surgery
Dynamic Procedures with Regional Muscle Transposition
Static Procedures with Slings
Free Microvascular Flaps
Adjuvant Procedures
39 Morbidity of Treatments
Introduction
Transient and Permanent Facial Nerve Palsy
Salivary Fistula and Sialocele
Gustatory Sweating
Facial Depression Deformity
Scar Cosmesis
Paresthesia in the Ear Region
Lingual or Hypoglossal Nerve Injury
40 Trauma-Induced Problems in the Salivary Glands
Introduction
Clinical Anatomy
Definition
Epidemiology
Clinical Features
Diagnostic Work-Up
Treatment
Late Sequelae of Injury
41 Quality of Life in Salivary Gland Diseases
Introduction
Definition and Concept
Measurement
Specific Problems in Salivary Gland Diseases
Measures to Improve Quality of Life
42 Influence of (Chemo-) Radiotherapy on Salivary Gland Function and Its Impact on Quality of Life
Introduction
General Aspects
Xerostomia after Radiotherapy
Dose–Response Curves
Radiation Techniques for Sparing the Salivary Glands
Amifostine and Radiation-Induced Xerostomia
Pilocarpine for Preserving Parotid Function
43 Salivary Gland Transplantation
Introduction
Definition
Physiology and Pathophysiology
Indications and Patient Selection
Diagnostic Work-Up
Patient Information and Consent
Anesthesia and Positioning
Operative Steps
Postoperative Care
Complications
Outcome
44 Salivary Gland Regeneration and Tissue Engineering
Introduction
Epidemiology and Etiology of Salivary Gland Hypofunction
Morphology and Mechanisms of Postradiotherapy Salivary Gland Hypofunction
Current Treatment Modalities for Xerostomia
Experimental Treatments
Future Trends
45 Medicolegal Issues
Introduction
Definition of Negligence
The Steps in a Medical Negligence, Tort-Based Claim
No-Fault Compensation Schemes
Duty of Care
Standard of Care
Consent
Causation
How to Avoid Being Sued
Special Issues Concerning Salivary Gland Surgery
46 New Developments in Molecular Biology
List of Abbreviations
Introduction
Recent and New Developments
Conclusions and Future Developments
People also search for Salivary Gland Disorders and Diseases Diagnosis and Management 1st:
thieme: salivary gland disorders and diseases
diseases associated with salivary glands
thyroid disease and salivary glands
diseases of the salivary glands symptoms
salivary gland diseases and disorders
You may also like…
eBook PDF
Atlas of Salivary Gland Pathology 1st edition by JoaquÃn GarcÃa ISBN 3319090208 978-3319090207